接着,请大家可以检查看看,目前喜欢练游泳的你是否有下列症状:
颈部伤害的症状
颈部和颈椎伤害可以区分为神经根病变(radiculopathy)、神经根炎(radiculitis)、椎间盘突出(herniated or bulging disc)或椎间盘退化症(degenerative disc disease with symptoms),这些症状可能包含:
放射状疼痛(radiating pain)
手臂的麻痺(numbness)或刺痛(tingling)
因为转动或伸展头部造成的肩膀夹挤痛
明显丧失转动头部的能力
突发的手臂无力感或肌肉萎缩。
下背与腰椎伤害的症状
下背或腰椎的伤害,例如神经根病变、神经根炎、腰椎狭窄(spinal stenosis)、椎间盘突出、椎间盘退化症和坐骨神经痛(sciatica),这些症状可能包含:
放射状疼痛
下背部在运动中或之后的麻木和刺痛感
练泳过后坐下时所感到的臀部(buttocks)疼痛感,或是突发的小腿或膝盖的无力感。
预防这些症状的注意事项与训练方式
预防游泳时的嵴椎伤害,需要特别注意铁人三项或游泳选手在游泳时,是否偏重单边换气或是左右手两侧的肌力发展不平均。运动时使用嵴椎时要注意嵴椎动作的完整性。对于一位每日工作于同一地点、需要进行长时间训练的铁人三项选手来说,加强肌力训练和多伸展是很重要的。以下有一些运动可以帮助你保持嵴椎的可动性和对称性:
颈部旋转伸展(Neck Rotation Stretch)
用你的左手抓住你头的右方,并且往你的左肩膀的方向轻压,记得保持双肩垂下和放松。你应该感觉到右侧颈部的舒适感,并且绝不要让自己感到疼痛、麻目或无力。对于一个静态伸展(static stretch)而言,记得保持伸展一分钟然后换边。两边都要施作三组。如果你在游泳之前做动态伸展(dynamic stretch),请重复多次的伸展并且不要在意角度。
(a)先伸展颈部右侧;(b) 接着再伸展颈部左侧
坐在椅子上或瑜珈球上作躯干旋转(Seated trunk rotation on a chair or physioball)
臀部坐在瑜珈球上,并且保持膝盖、双手和背部保持一直线。举起你的手到你的头的后面或两侧。当你旋转躯干的时候尽力使用你的腹部、核心肌肉,并且注意不要让臀部、膝盖和双手移动。在做动作时你会感受到上背和肩膀有伸展到,保持伸展姿势一分钟,然后换边,一边要做三次。
坐姿躯干旋转
站立时手臂过头向后伸展(Standing back extension with arms overhead)
站立并且将手举过头,保持手肘和手臂伸直成一直线。轻轻地依序伸展你的嵴背、颈部最后是头部。思考个别从脚底到头顶移动嵴椎骨(vertebrae),并且感受嵴椎、核心肌力的伸展和肩膀靠拢。过程中,你绝不让自己感觉到痛、麻木、刺痛或是昏眩,并且保持伸展姿势一分钟后放松,总共作三组。
站立时手臂过头向后伸展
出处:Joe Friel,Jim Vance, editors (2013). Triathlon science.,464, 465, 466, 467. United States of America: Human Kinetics.
原文:
Spine and neck injuries
Although less common in swimming, a spinal injury may be more deblitating than an injury to the shoulder. Typically, spinal injuries become chronic in nature because they are adjusted or compensated for by the athlete’s unknowingly changing the stroke pattern (i.e., turning out of one side only or rotating the trunk instead of the neck). Posture and positioning of the neck and shoulders during swimming, much like in sitting, plays a significant role in the amount of stress placed on the spine. In most cases, spinal injuries resulting from swimming are related to the aggravation of an already pathological spine by prolonged spinal positioning, meaning that the athlete has had a known or unknown spinal injury in the past.
Neck or cervical injuries can be described as radiculopathy, radiculitis, herniated or bulging disc, or degenerative disc disease with symptoms that may include radiating pain, numbness or tingling into the arm, scapular(shoulder blade) pain with turning or extending the head, a noticeable loss of head-turning ability, or sudden arm weakness or muscle atrophy. Low-back or lumbar injuries such as radiculopathy, radiculitis, spinal stenosis, herniated or bulging disc, degenerative disc disease, and sciatica may also include radiating pain, numbness or tingling in the lower extremity during or after swim, pain in the buttocks while sitting after a swim workout, or sudden leg or ankle weakness.
Preventing spinal injury in swimmers requires particular attention to the triathlete’s symmetry of spinal rotation, mobility into extension, and overall posture. Exercise should focus on moving the spine with full range of motion. Exercise are particularly important for triathletes who have day jobs that require prolonged sitting or standing in one place. The following recommendations and exercises will help keep the spine mobile and its movement symmetrical.
Neck Rotation Stretch
Grab the right side of your head with your left hand and gently pull your head toward your left shoulder. Keep both shoulders down and relaxed. You should feel stretch on the right side of the neck. You should nerve feel pain, numbness, or tingling. For a static stretch, hold the stretch for 1 minute and switch sides. Perform three stretches on each side.
If you perform stretch prior to swimming, perform dynamic stretches. Repeat the stretch multiple times without holding the stretch at the end range.
Seated Trunk Rotation on a Chair or Physioball
Sit on a physioball with the hips, kness, and feet in line and the back straight. Lift your arms so that your hands are behind or to the sides of your head. Engage your abdominal muscles and core as you rotate your trunk as far as possible. Do not allow the hips, kness, or feet to move. Feel the stretch around your midback and shoulders. Hold the stretch for 1 minute then stretch to the other side. Perform three stretches on each side.
Standing Back Extension With Arms Overhead
Stand and lift your arms overhead, keeping the elbows straight and arms in. Gently extend your spine back, extending the neck and head last. Think about moving each vertebrae individually from the bottom to the top. Feel the stretch in the spine, abdominal muscles, and shoulders blades. You should never feel pain, numbers, tingling, or dizziness. Hold the stretch for 1 minute then release. Stretch three times.
读后心得与启发:
在《运动伤害图解圣经》中,对于游泳这项运动有颈部和嵴椎的运动伤害详细的介绍,在此我以更有系统的方式整理出来、并且附上相关示意图,读者们就可以更理解在游泳训练时对于颈部和嵴椎的伤害描述和预防方式(以下内容和图片,摘自DK Publishing:《运动伤害图解圣经》,台北市:旗标,2012,页40,56,60,220,240):
游泳时,头部快速的旋转会导致肌肉的拉伤,像是“颈部拉伤”。颈椎,位于嵴椎的最上段,这是一个连接颅骨与胸椎(嵴椎中段)的构造,包含七块骨头,周围被肌肉、肌腱与韧带所包围。(参考图四:颈部拉伤)所以“颈部拉伤”是颈椎周围肌肉、肌腱与韧带拉伤的统称,原因是从高处跌落、突然的撞击或扭转颈部会对颈椎上附着的肌肉、肌腱或韧带产生应力。这边可以想像成因为颈椎突然承受外来力量,因此导致周边组织受伤。
颈部拉伤
这边也推荐一个“徒手等张收缩(Manual Isometrics)”运动(见下图五的三个步骤),来帮助复健或是初期锻鍊颈部肌肉用。这个等张收缩的徒手颈部肌力训练,可用站姿或坐姿进行。对颈部受伤或是开始训练颈部的人而言,这是一个必要的复健运动。随着肌力的进步,可以结合弹力带或重量训练机器来提供颈部足够的负荷。
步骤一:双手十指交握于头部后方,颈部出力让头部像后顶住双手,保持手的位置不要移动。用力几秒钟,然后放松。
注意:1. 头部用力向后推,来抵抗阻力。2. 保持手部的位置
步骤二:掌根顶住头部侧面,颈部用力向侧面推,抵抗来自手的阻力。用力几秒钟后放松。然后换边进行。
注意:1. 颈部用力向侧面推,来抵抗阻力。2. 保持颈部不要移动头部
步骤三:将右手掌置于太阳穴,左手掌至于头部后方。头部向右方旋转施力,双手同时提供阻力,保持颈部直立,头部不要移动。用力几秒钟后放松。然后换边进行。
注意:1. 颈部抵抗阻力旋转。2. 保持颈部直立,不要移动头部
再来,快速的转身(茗杰註:像是游泳选手比赛时的转身蹬墙)可能会导致下背的“椎间盘突出”,此症状是因为在每一节嵴椎骨之间都垫着一块盘状软骨(椎间盘)作吸震与缓冲,这些软骨的中心是柔软的胶状物质,外围则由坚韧的纤维组织所包围,如果椎间盘受挤压而破裂或“滑动”(即椎间盘突出),内部的流体就会压迫到嵴神经根(参考图七:椎间盘突出)。
长时间的游泳训练也会对背部造成压力,有可能会对椎间盘造成伤害。下背部是椎间盘突出的好发部位,但也可能发生于嵴椎的任何一节,突出之后受到压迫的神经会造成下背痛与坐骨神经痛(或是从下背延伸至臀部、大腿、小腿的疼痛感)。
坐骨神经痛 椎间盘突出
坐骨神经痛:坐骨神经是人体最大的周边神经,从嵴椎的下段一路延伸到脚掌,受损伤时其所经之处都可能发生疼痛。
椎间盘突出:椎间关节是由两块嵴椎骨与其间的盘状软骨所构成,当椎间盘滑动时,邻近的神经就会被压迫
所以要预防这些病状的发生,平日的柔软度训练就显得重要
这边介绍一种柔软度训练方式:“阔背肌伸展(Lat Stretch)”(参考图八:阔背肌伸展(Lat Stretch)
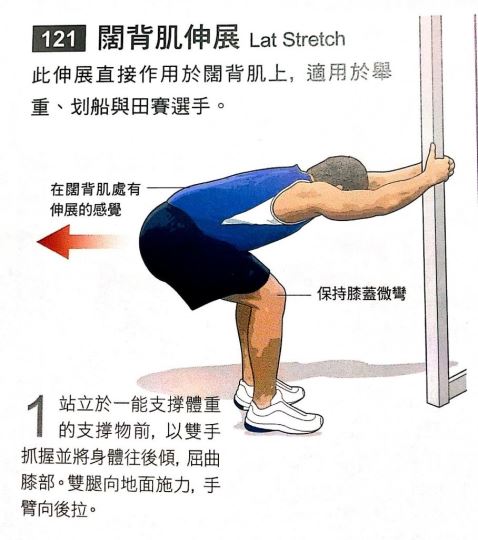
阔背肌伸展(Lat Stretch)
站立于一能支撑体重的支撑物前,以双手抓握并将身体往后倾。
屈曲膝部,双腿向地面施力,手臂向后拉
注意:1. 在阔背肌处有伸展的感觉。2. 保持膝盖微弯。
作者:庄茗杰/编辑:徐国峰
图片来源:Triathlon science与《运动伤害图解圣经》
耐力网相信训练是科学也是艺术,而训练的艺术,是科学化的极致表现。
奥运会马拉松://www.nduoke.com/paobushuju/olympic-games-marathon-results



